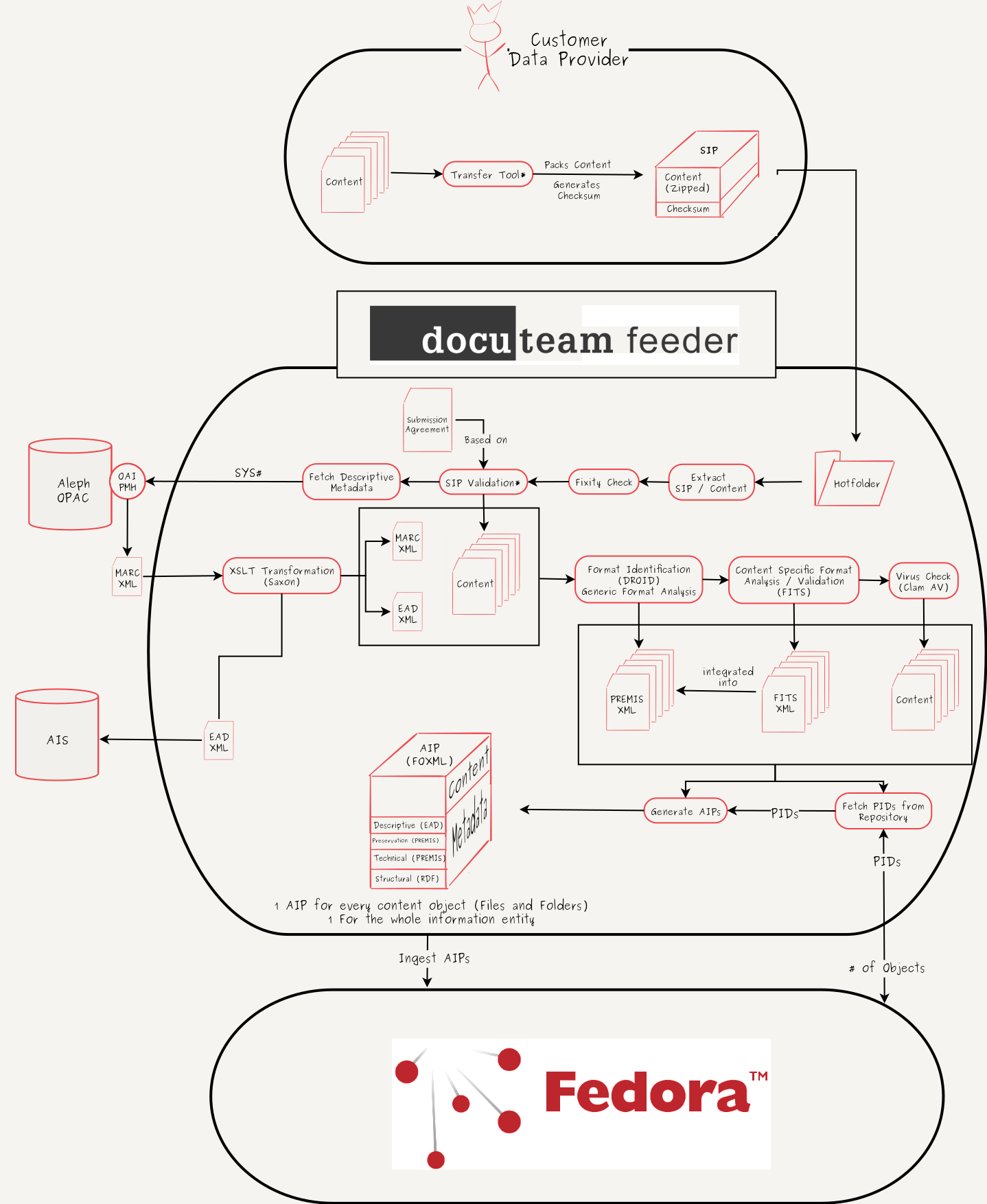
Workflow:Workflow for ingesting digitized books into a digital archive
Revision as of 12:08, 7 April 2017 by ChrisReinhart (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Upload file (Toolbox on left) and add a workflow image here or remove Category:COW Workflows ==Workflow Description== <div class="toccolours mw-coll...")
Upload file (Toolbox on left) and add a workflow image here or remove
Workflow Description
- The data provider provides his content as an input for the transfer tool (currently in development)
- The transfer tool creates a zip-container with the content and calculates a checksum of the container
- The zip-container and the checksum are bundled (another zip-container or a plain folder) and build the SIP
- The transfer tool moves the SIP to a registered, data provider specific hotfolder, which is connected to the ingest server
- As soon as the complete SIP has been transfered to the ingest server, a trigger is raised and the ingest workflow starts
- The SIP gets unpacked
- The included zip container is validated according to the provided checksum. If this fixity check fails, the data provider is asked to reingest his data.
- The content and the structure of the content are validated against the submission agreement, that was signed with the data provider (this step is currently in development)
- Based on the OPAC-systemnumber (encoded in the content filename) descriptive metadata is fetched from the library's OPAC over its OAI-PMH interface
- The OPAC returns a MARC.XML-file.
- The MARC.XML-file is mapped into a EAD.XML-file by a xslt-transformation
- The EAD.XML is exported to a designated folder for pickup by the archival information system
- Every content file is analysed by DROID for format identification and basic technical metadata is extracted (e.g. filesize)
- The output of this analysis is saved into a PREMIS.XML-file (one PREMIS.XML per content object).
- Every content file is validated and analysed by FITS and content specific technical metadata is extracted.
- The output of this analysis (FITS.XML) is integrated into the existing PREMIS.XML-files.
- Each content file is scanned for viruses and malware by Clam AV.
- For each content object and for the whole information entity (the book) a PID is fetched from the repository
- For each content object and for the whole information entity an AIP is generated. This process includes the generation of RDF-tipples, that contain the relationships between the objects.
- The AIPs are ingested into the repository
List of Tools
- 7-Zip - Pack and unpack content / SIPs
- docuteam feeder - Workflow- and Ingestframework
- cURL - Fetch MARC.XML per http
- Saxon - MARC.XML to EAD.XML mapping
- DROID - Format Identification and generation of basic technical metadata
- FITS_(File_Information_Tool_Set) - Generation of specific, content aware technical metadata
- Clam AV - Virus check
- Fedora_Commons - Digital Repository