Difference between revisions of "Workflow:Archiving outputs of 3D scanning"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
<!-- Describe what your workflow is for - i.e. what it is designed to achieve, what the organisational context of the workflow is, and what content it is designed to work with --> | <!-- Describe what your workflow is for - i.e. what it is designed to achieve, what the organisational context of the workflow is, and what content it is designed to work with --> | ||
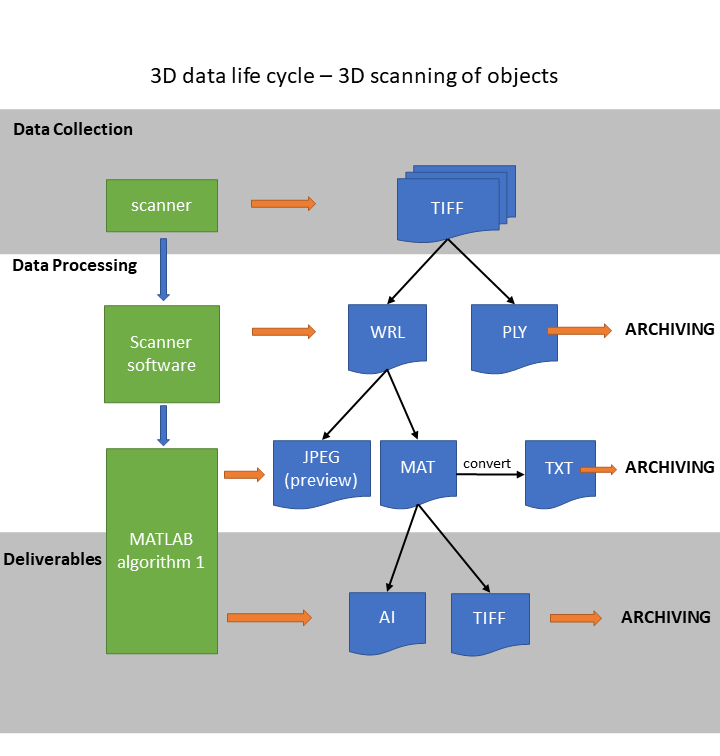
The workflow documents the process of creating 3D models (of objects) and their derivatives by a stereo-scanner, and specifies which outputs can and need to be archived. | The workflow documents the process of creating 3D models (of objects) and their derivatives by a stereo-scanner, and specifies which outputs can and need to be archived. | ||
| − | # | + | # Data acquisition - scanning (and archiving?) |
| − | # | + | # Data processing |
| − | ## | + | ## Generating and archiving 3D mesh |
| − | ## | + | ## Positioning of the object based on its geometric properties |
| − | # | + | # Output - generating and archiving standard drawings or set of views on the model. |
==Evaluation/Review== | ==Evaluation/Review== | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 28 February 2022
Workflow Description
Purpose, Context and Content
The workflow documents the process of creating 3D models (of objects) and their derivatives by a stereo-scanner, and specifies which outputs can and need to be archived.
- Data acquisition - scanning (and archiving?)
- Data processing
- Generating and archiving 3D mesh
- Positioning of the object based on its geometric properties
- Output - generating and archiving standard drawings or set of views on the model.
Evaluation/Review
Further Information
Scanner software: https://www.polymetric.de/index.php?id=44&L=2 Core publications: Karasik, A. and Smilansky U. 2011. Computerized morphological classification of ceramics. Journal of Archaeological Science 38(10):2644-2657. Karasik, A. and Smilansky U. 2008. 3D scanning technology as a standard archaeological tool for pottery analysis: practice and theory. Journal of Archaeological Science 35(5):1148-1168.